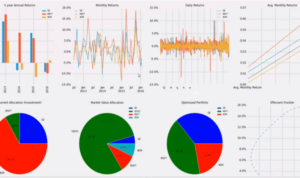
Get ready to dive into the world of financial asset classes where stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities come alive in a thrilling narrative that will keep you on the edge of your seat.
Let’s explore the characteristics, types, and allocation strategies of these assets to uncover the mysteries of investment portfolios.
Introduction to Financial Asset Classes
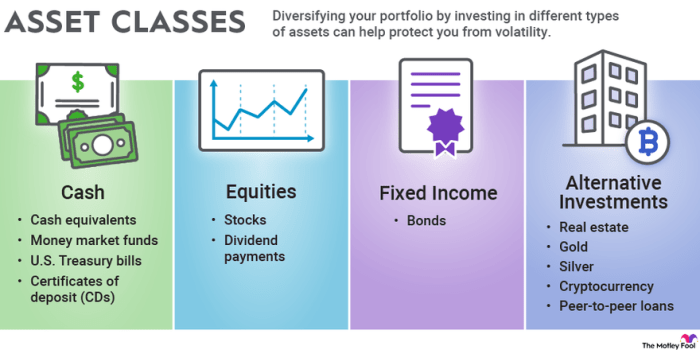
Financial asset classes are different categories of assets that investors can invest in, each with its own characteristics and risk-return profiles. These asset classes are essential components of investment portfolios as they help investors diversify their investments and manage risk. Diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce the impact of any single asset’s performance on the overall portfolio.
Common Financial Asset Classes
- Stocks: Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for capital appreciation and dividends.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing fixed income to investors.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments include properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial real estate, offering potential rental income and capital appreciation.
- Commodities: Commodities include physical goods like gold, oil, or agricultural products, providing diversification and a hedge against inflation.
Characteristics of Different Asset Classes
When it comes to investing, understanding the characteristics of different asset classes is crucial. Each asset class has its own risk-return profile, liquidity level, and susceptibility to market volatility and economic conditions.
Risk-Return Profiles
Different asset classes offer varying levels of risk and potential return. Generally, higher risk investments such as stocks have the potential for higher returns, but also come with greater volatility. On the other hand, lower risk investments like bonds offer more stability but lower potential returns.
Liquidity Differences
Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting its price. Cash is the most liquid asset, while real estate and private equity are less liquid. Stocks and bonds fall somewhere in between. Understanding the liquidity of an asset class is important for investors who may need to access their funds quickly.
Impact of Market Volatility and Economic Conditions
Market volatility and economic conditions have a significant impact on different asset classes. For example, during times of economic uncertainty, investors may flock to safe-haven assets like gold or Treasury bonds, causing their prices to rise. On the other hand, riskier assets like stocks may experience sharp declines during market downturns. It is essential for investors to consider these factors when constructing a diversified portfolio.
Types of Financial Asset Classes
In the world of investing, financial asset classes can be broadly categorized into traditional and alternative asset classes. Each type offers unique characteristics and investment strategies for investors looking to diversify their portfolio.
Traditional Asset Classes
Traditional asset classes include stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for capital appreciation through dividends and price appreciation. Bonds, on the other hand, are debt securities issued by corporations or governments, providing fixed income through interest payments. Cash equivalents are low-risk, highly liquid assets such as money market funds.
- Stocks: Investors can gain exposure to stocks through individual company shares or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track stock indexes like the S&P 500.
- Bonds: Investors can invest in bonds directly or through bond funds, which offer diversification across different types of bonds.
- Cash Equivalents: Money market funds provide a safe and easily accessible option for investors looking to park their cash temporarily.
Alternative Asset Classes
Alternative asset classes, such as private equity, hedge funds, real estate, and commodities, offer diversification beyond traditional investments and often come with higher risk and return potential.
- Private Equity: Investors can gain exposure to private companies through private equity funds, which invest in private companies with the potential for high returns but limited liquidity.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds are actively managed investment funds that use various strategies to achieve returns, often with higher fees and less regulation compared to traditional investments.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can include direct ownership of properties, real estate investment trusts (REITs), or real estate crowdfunding platforms.
- Commodities: Investors can invest in commodities like gold, oil, or agricultural products through commodity futures, exchange-traded products, or physical ownership.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation is a crucial concept in portfolio management that involves dividing investments among different asset classes to achieve a balance between risk and return. By spreading investments across various asset classes, investors can minimize risk and optimize returns over time.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation is a long-term investment strategy where the allocation of assets is based on the investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. This model typically involves setting target allocations for different asset classes and periodically rebalancing the portfolio to maintain those targets.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions and economic outlook. This strategy allows investors to take advantage of short-term opportunities or mitigate risks in specific asset classes.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation is a more flexible approach that allows for changes in asset allocation based on changing market conditions, economic forecasts, or investment objectives. This model requires active management and monitoring of the portfolio to adjust allocations as needed.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation Decisions
– Risk Tolerance: Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate more assets to equities or other high-risk investments, while those with lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative allocation.
– Investment Goals: The specific financial objectives of an investor, such as retirement savings or wealth preservation, will influence the allocation of assets in the portfolio.
– Time Horizon: The length of time an investor plans to hold investments will impact asset allocation decisions. Longer time horizons may allow for more aggressive allocations, while shorter horizons may require a more conservative approach.