Fixed-income investments set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we dive deeper into the world of fixed-income investments, we uncover the hidden gems and potential pitfalls that come with this type of investment.
What are Fixed-Income Investments?
Fixed-income investments are financial instruments that generate a fixed return in the form of interest payments over a specific period of time. These investments are typically considered safer than stocks because they provide a predictable income stream and return of principal at maturity.
Fixed-Income Securities
Fixed-income securities are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, or other entities to raise capital. Investors who purchase these securities are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of the principal amount at the end of the investment period.
- Government Bonds: These are issued by government entities to finance public projects and are considered one of the safest fixed-income investments.
- Corporate Bonds: These are issued by companies to raise capital for business operations and expansion. They offer higher returns than government bonds but come with higher risk.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits offered by banks with fixed terms and interest rates. They are insured by the FDIC up to a certain limit, making them a low-risk investment option.
- Treasury Securities: These are debt securities issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury and are considered one of the safest investments in the world.
Benefits of Fixed-Income Investments
Investing in fixed-income securities offers several advantages that can benefit investors looking for stability and consistent returns in their portfolio. These investments provide a predictable stream of income, help diversify a portfolio, and offer a lower level of risk compared to other asset classes.
Stability in Portfolio
Fixed-income investments, such as bonds and CDs, are known for their stable returns and low volatility. They provide a reliable source of income that can help balance out the fluctuations in the stock market. This stability can be particularly attractive to investors looking to preserve capital and generate steady returns over time.
Risk-Return Profile
When compared to other asset classes like stocks or real estate, fixed-income investments typically have a lower risk-return profile. While the returns may be more modest, the level of risk associated with these investments is also lower. This makes fixed-income securities a valuable addition to a well-rounded investment portfolio, providing a cushion against market volatility and potential losses.
Types of Fixed-Income Investments
Government bonds, corporate bonds, and bond funds are common types of fixed-income investments that investors can consider when looking to add stability and income to their portfolios.
Government Bonds
Government bonds are debt securities issued by a government to raise capital. Investors essentially lend money to the government in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the bond’s face value at maturity. These bonds are considered low-risk investments since they are backed by the government’s ability to tax its citizens to repay the debt. Treasury bonds are popular government bonds issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Corporate Bonds
Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by corporations to raise funds for various purposes, such as expansion or operations. When investors purchase corporate bonds, they are essentially lending money to the issuing corporation in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the bond’s face value at maturity. Corporate bonds typically offer higher yields compared to government bonds but come with higher risks due to the creditworthiness of the issuing company.
Differences Between Bonds, Bond Funds, and Bond ETFs
- Bonds: Individual bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. Investors hold these bonds until maturity to receive interest payments and the return of the bond’s face value.
- Bond Funds: Bond funds pool investors’ money to invest in a diversified portfolio of bonds. Investors in bond funds receive income through interest payments and potential capital appreciation.
- Bond ETFs: Bond exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to bond funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer diversification and liquidity, with prices fluctuating throughout the trading day.
Risks Associated with Fixed-Income Investments
Investing in fixed-income securities comes with its own set of risks that investors should be aware of. Two key risks associated with fixed-income investments are interest rate risk and credit risk. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to the potential impact of changes in interest rates on the value of fixed-income investments. When interest rates rise, the value of existing fixed-income securities tends to decrease. This is because newly issued securities offer higher yields, making existing bonds with lower yields less attractive. On the other hand, when interest rates fall, the value of existing fixed-income securities tends to increase. Investors holding fixed-income investments until maturity may not be as affected by interest rate fluctuations, as they will continue to receive the promised payments. However, those looking to sell their securities before maturity may experience losses if interest rates have moved unfavorably.
- As interest rates rise, bond prices fall.
- Longer-term fixed-income securities are more sensitive to interest rate changes than short-term securities.
- Callable bonds may be more susceptible to interest rate risk as issuers can redeem them early when interest rates are low.
Credit Risk
Credit risk, also known as default risk, refers to the risk of the issuer of fixed-income securities failing to make interest payments or repay the principal amount. This risk is higher for securities issued by entities with lower credit ratings. Investors demand higher yields for securities with higher credit risk to compensate for the increased likelihood of default. Credit risk can significantly impact the value of fixed-income securities, with defaults leading to potential losses for investors.
- Government bonds are generally considered to have lower credit risk compared to corporate bonds.
- Ratings agencies assess the creditworthiness of bond issuers and assign credit ratings based on their findings.
- Diversifying fixed-income investments across issuers and industries can help mitigate credit risk.
Factors to Consider When Investing in Fixed-Income
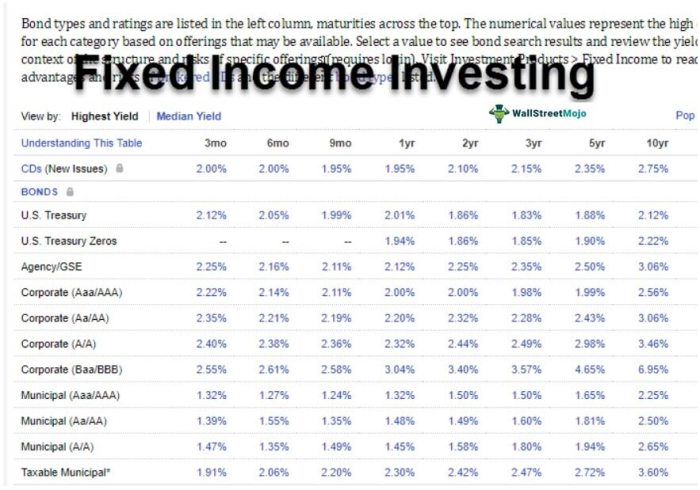
Investing in fixed-income securities requires careful consideration of various factors to maximize returns while managing risks effectively.
Credit Ratings in Fixed-Income Investing
Credit ratings play a crucial role in fixed-income investing as they provide insight into the creditworthiness of the issuer. Higher credit ratings indicate lower default risk, but they may also come with lower yields. On the other hand, lower-rated bonds offer higher yields but carry higher default risk. It is essential to balance risk and return based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Building a Diversified Fixed-Income Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing risk in a fixed-income portfolio. By investing in a variety of bonds with different maturities, issuers, and credit ratings, you can spread risk and minimize the impact of any single bond defaulting. Consider diversifying across various sectors and geographic regions to further reduce risk. Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.