Diving into Understanding asset classes, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with American high school hip style that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence.
Get ready to explore the world of asset classes and how they play a crucial role in investment portfolios.
What are Asset Classes?
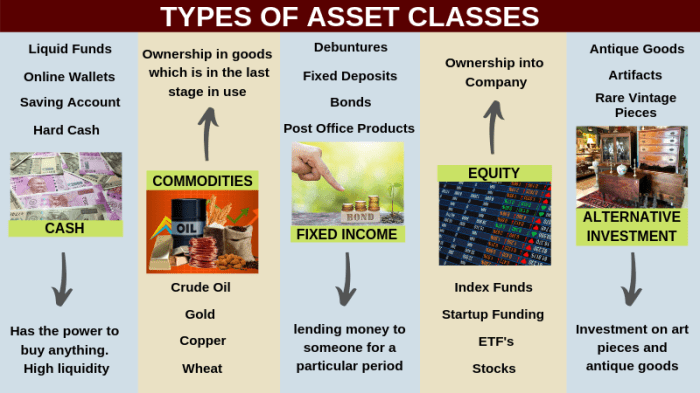
Asset classes are categories of investments that have similar characteristics and behave in a similar way in the market. They are essential for investors to diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively. Examples of asset classes include stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash equivalents.
Importance of Asset Classes
Asset classes play a crucial role in investment portfolios by spreading out risk and enhancing returns. By investing in a variety of asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall portfolio. Each asset class has its own risk-return profile, so having a mix of different asset classes helps to achieve a balance between risk and reward.
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for high returns, but come with higher risk due to market fluctuations.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations that provide a fixed income stream, offering lower risk compared to stocks.
- Real Estate: Includes properties like residential, commercial, and industrial real estate, offering potential for rental income and capital appreciation.
- Commodities: Raw materials or primary agricultural products, such as gold, oil, or wheat, which can act as a hedge against inflation and provide portfolio diversification.
- Cash Equivalents: Highly liquid and low-risk investments like treasury bills or certificates of deposit, providing stability and easy access to funds.
Types of Asset Classes
Investors have a variety of asset classes to choose from when building their investment portfolios. Each asset class comes with its own characteristics, risk profiles, and performance history. Let’s take a closer look at some major asset classes:
Stocks
Stocks, also known as equities, represent ownership in a company. When you buy shares of a company’s stock, you become a part owner of that company. Stocks are known for their potential to provide high returns, but they also come with high volatility and risk. The performance of stocks can be influenced by factors such as company earnings, economic conditions, and market sentiment.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations to raise capital. When you buy a bond, you are essentially loaning money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the bond’s face value at maturity. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks, but they offer lower returns. The performance of bonds is affected by interest rates, credit quality, and the issuer’s financial health.
Real Estate
Real estate refers to physical properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, and land. Investing in real estate can provide rental income and potential appreciation in property value. Real estate investments are typically less liquid than stocks and bonds, but they can offer diversification and a hedge against inflation. The performance of real estate is influenced by factors such as location, demand-supply dynamics, and economic trends.
Commodities
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that are traded on exchanges. Common commodities include gold, oil, wheat, and coffee. Investing in commodities can help diversify a portfolio and provide a hedge against inflation and currency fluctuations. Commodities are known for their price volatility, which can be influenced by factors such as supply-demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and weather conditions.
Factors Influencing Asset Class Selection
When choosing asset classes for investment, several factors come into play that can significantly impact the decision-making process.
Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Investors need to consider their investment goals and risk tolerance when selecting asset classes. Those with a higher risk tolerance might opt for more volatile investments like stocks, while those with a lower risk tolerance might prefer safer options like bonds or real estate.
Economic Conditions
The prevailing economic conditions can also influence the choice of asset classes. For example, during periods of economic uncertainty, investors may flock to gold or other safe-haven assets. In contrast, in a booming economy, they might lean towards stocks for higher returns.
Age and Time Horizon
Age and time horizon play a crucial role in determining asset allocation. Younger investors with a longer time horizon can afford to take more risks and invest in growth-oriented assets. On the other hand, older investors nearing retirement may prioritize capital preservation and opt for more stable investments.
Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to managing your investments, asset allocation strategies play a crucial role in determining the mix of assets in your portfolio. These strategies help investors achieve their financial goals by balancing risk and return based on their investment objectives.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves setting a long-term target mix of assets based on an investor’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. This strategy aims to maintain a diversified portfolio that aligns with the investor’s overall investment strategy.
- Strategic asset allocation typically involves rebalancing the portfolio periodically to maintain the target asset allocation.
- Investors often use strategic asset allocation as a buy-and-hold strategy to ride out market fluctuations.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions and economic outlook. This strategy allows investors to take advantage of short-term opportunities or mitigate risks in the market.
- Investors using tactical asset allocation may shift their asset allocation based on market trends or changes in economic indicators.
- Tactical asset allocation requires active monitoring of the market and the ability to make quick decisions to capitalize on opportunities.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation combines elements of both strategic and tactical asset allocation strategies. This approach allows investors to adjust their asset allocation based on changing market conditions while maintaining a long-term investment focus.
- Dynamic asset allocation strategies often use a rules-based approach to determine when to adjust the portfolio’s asset mix.
- Investors using dynamic asset allocation aim to capture market opportunities while managing risk through active portfolio management.
Rebalancing is a critical component of asset allocation as it ensures that the portfolio’s asset mix stays aligned with the investor’s goals and risk tolerance.
Modern portfolio theory, developed by Harry Markowitz, provides a framework for asset allocation decisions by emphasizing the importance of diversification and the relationship between risk and return in a portfolio.
Real-World Applications
In the real world, successful asset class selection can make a significant impact on investment portfolios. Let’s explore some case studies and examples of how asset classes perform in different market conditions.
Case Study 1: Successful Asset Class Selection
- During the 2008 financial crisis, investors who allocated a portion of their portfolio to gold saw significant gains as the price of gold surged amidst economic uncertainty.
- Real estate investment trusts (REITs) have historically performed well during periods of low interest rates, providing a steady income stream for investors.
Impact of Geopolitical Events
- Geopolitical events such as trade wars, conflicts, and elections can have a significant impact on asset class performance.
- For example, when tensions rise between countries, safe-haven assets like government bonds and gold tend to see increased demand as investors seek stability.
Macroeconomic Trends and Asset Class Returns
- Macroeconomic trends such as inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth can influence the relative returns of different asset classes.
- During periods of high inflation, real assets like commodities and real estate tend to outperform while fixed-income investments may struggle to keep up with rising prices.